Monitoring carnosine uptake by RAW 264.7 macrophage cells using microchip electrophoresis with fluorescence detection
Abstract
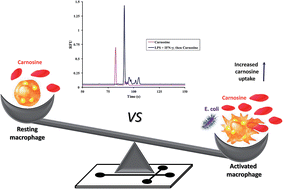
Carnosine, a dipeptide found in a variety of tissues, is believed to possess antioxidant properties. It serves as a scavenger of reactive nitrogen and oxygen species (RNOS), which are important stress mediators of pro-inflammatory conditions and can lead to macrophage activation. In this study, intracellular concentrations of carnosine in murine RAW 264.7 macrophage cells were determined using microchip electrophoresis with laser-induced fluorescence detection following derivatization with naphthalene-2,3-dicarboxaldehyde and cyanide. The method was linear from 25 nM to 5 μM with a limit of detection in cell lysate samples of 65 nM. Using the method of standard additions, the basal intracellular content of carnosine in macrophage cells was determined to be 0.079 ± 0.02 nmol per 106 cells. The uptake of carnosine by these cells was then investigated under both physiological and pro-inflammatory conditions. There was a 2.8-fold increase in carnosine uptake for macrophages exposed to lipopolysaccharides and interferon-γ prior to incubation, compared to the controls. This suggests that macrophages may use carnosine uptake as a defense mechanism under pro-inflammatory conditions. Future studies will investigate the role of the carnosine transporter in carnosine uptake and its possible correlation with cell morphological changes observed after stimulation.
- This article is part of the themed collections: Celebrating Excellence in Research: 100 Women of Chemistry and In memory of Craig Lunte


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...