Screening of neuraminidase inhibitors from the leaves of Syringa velutina Kom. via compound fractionation and in vitro activity evaluation†
Abstract
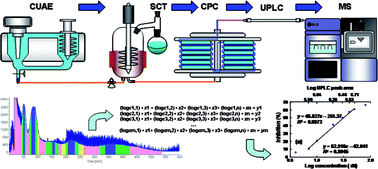
A novel hyphenated technique comprised of circulating ultrasound-assisted extraction (CUAE) coupled with an online solvent concentration tank (SCT), centrifugal partition chromatography (CPC), ultra-high performance liquid chromatography (UPLC), and mass spectrometry (MS) was established. Chemical compounds from the leaves of Syringa velutina Kom. were extracted, isolated, and fractionated by CPC and then analyzed using the hyphenated technique. In this study, 60% aqueous ethanol was used as the CUAE solvent. After extraction, the extraction solution was pumped into the SCT and concentrated. The concentrated solution was then pumped into the CPC column and eluted using a biphasic solvent system of ethyl acetate/n-butanol/acetonitrile/water (0.8 : 0.2 : 0.15 : 1.0, v/v/v/v). The CPC fractions were monitored using a UV detector at 250 nm and an online UPLC/PDA system at 5 min intervals. The CPC fractions were collected by a sample loop via a six-port valve, and the neuraminidase inhibitory activities of the CPC fractions were analyzed using a fluorescence method. The pure compounds were analyzed directly, and the activities of the mixed compounds were calculated using mathematical equations. The results indicated that the inhibition rates of syringin, oleuropein aglycone, luteoloside, and syringopicroside were above 50.00% at a concentration of 40 μM, and they have the potential for further development. These results were proven using authentic standards.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...