Electrochemical reactive oxygen species detection by cytochrome c immobilized with vertically aligned and electrochemically reduced graphene oxide on a glassy carbon electrode†
Abstract
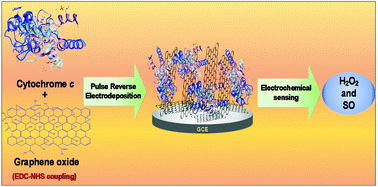
A new amperometric biosensor for hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) and superoxide anion (SO) has been developed. The biosensor developed uses cytochrome c (Cyt c) modified glassy carbon electrodes coupled with electrochemically reduced graphene oxide (ErGO). To immobilize Cyt c, the “one step” electrochemical deposition of vertically aligned and ErGO (VAErGO) has been performed by using a pulse reverse technique, thus resulting in a very simple and efficient system. The well-established vertical alignment of ErGO was confirmed by atomic force microscopy and the electrochemical characteristics of the biosensor were investigated by cyclic voltammetric, electrochemical impedance spectroscopy and amperometric techniques. The surface coverage (Γ) of immobilized Cyt c was effectively increased by the vertical alignment of ErGO and found to be 1.03 × 10−10 mol cm−2. The direct electron transfer property of Cyt c was also improved by VAErGO and the heterogeneous electron transfer rate constant (ket) was estimated to be 6.40 s−1. To detect H2O2 and SO, amperometric measurements were carried out at different operating potentials (0.0 V vs. Ag/AgCl for H2O2 and +0.2 V for SO). The sensitivity and detection limit for H2O2 were found to be 46.3 μA mM−1 cm−2 and 2.3 μM, and for SO were found to be 32.1 μM nA−1 cm−2 and 6.84 nM s−1, respectively. Additionally, the designed biosensor exhibited strong anti-interference ability and satisfactory reproducibility.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...