3rd generation poly(ethylene imine)s for gene delivery†
Abstract
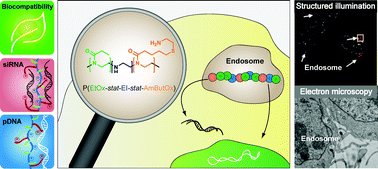
Cationic polymers play a crucial role within the field of gene delivery offering the possibility to circumvent (biological) barriers in an elegant way. However, polymers are accompanied either by a high cytotoxicity or low efficiency. In this study, a series of high molar mass poly(2-oxazoline)-based copolymers was synthesized introducing 2-ethyl-2-oxazoline, ethylene imine, and primary amine bearing monomer units representing a new generation of poly(ethylene imine) (PEI). The potential of these modified PEIs as non-viral gene delivery agents was assessed and compared to linear PEI by studying the cytotoxicity, the polyplex characteristics, the transfection efficiency, and the cellular uptake using plasmid DNA (pDNA) as well as small interfering RNA (siRNA). High transfection efficiencies, even in serum containing media, were achieved using pDNA without revealing any cytotoxic effects on the cell viability at concentrations up to 1 mg mL−1. The delivery potential for siRNA was further investigated showing the importance of polymer composition for different genetic materials. To elucidate the origins for this superior performance, super-resolution and electron microscopy of transfected cells were used, identifying the endosomal release of the polymers as well as a reduced protein interaction as the main difference to PEI-based transfection processes. In this respect, the investigated copolymers represent remarkable alternatives as non-viral gene delivery agents.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...