Titanium alkylphosphate functionalised mesoporous silica for enhanced uptake of rare-earth ions†
Abstract
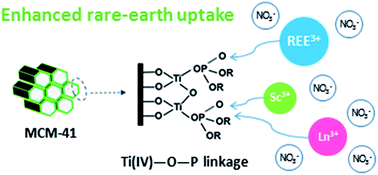
The separation of rare-earth elements (REEs) is usually carried out by a multi-stage solvent extraction process utilising organophosphorus extractants. Inspired by the structure of the solvating extractant tri-n-butyl phosphate (TBP), new sorbents were designed by covalently attaching short n-alkyl chains (ethyl, n-propyl and n-butyl) to titanium(IV) phosphate functionalised mesoporous MCM-41 silica by a layer-by-layer grafting route. Mesoporous MCM-41 silica served as a versatile porous support and the grafted titanium(IV) derivatives provided enhanced acid stability and solvating extraction capability. Various characterisation methods including solid-state 13C, 29Si and 31P magic-angle spinning (MAS) nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) and simultaneous thermogravimetry and differential scanning calorimetry-mass spectroscopy (TG/DSC-MS) were used to confirm the ligand attachment. The hybrid materials showed a better uptake of rare-earth ions from nitrate feed solution than the unmodified inorganic material. The optimal separation factor (SF) obtained for scandium–lanthanum separation is in excess of 100 000 at pH 2.1. The SFs calculated for dysprosium–neodymium are approximately 3, which is comparable to that of TBP in a typical solvent extraction setup. This study provides a new strategy to design inorganic–organic hybrid sorbents based on the structure of organophosphorus extractants via metal(IV)–O–P bonds.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...