Ionic liquid-assisted synthesis of α-Fe2O3 mesoporous nanorod arrays and their excellent trimethylamine gas-sensing properties for monitoring fish freshness†
Abstract
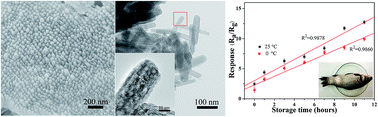
Large-scale and well-aligned α-Fe2O3 mesoporous nanorod arrays in situ deposited on ceramic tubes have been successfully synthesized by an ionic liquid (IL)-assisted hydrothermal reaction followed by calcination. The mesoporous sizes of the nanorods can be adjusted by changing the calcination temperature. Such an in situ assembled α-Fe2O3 mesoporous nanorod array sensor exhibited not only high sensitivity, short recovery time and good reproducibility to trimethylamine (TMA), but also a good linear relationship in a ppm level concentration range (0.1–100 ppm). Furthermore, the sensor was evaluated for a fast analysis of the primary volatiles of Carassius auratus (0–11 h) which have been analyzed using headspace solid phase microextraction (HS-SPME) and gas chromatography-mass spectrometry (GC-MS). Such α-Fe2O3 mesoporous nanorod arrays showed considerable potential in the identification of fish freshness. The superior gas-sensing properties of the obtained nanostructures should be attributed to the uniform mesoporous structure in the ordered nanorod arrays with a large specific surface area, as well as an appropriate amount of residual functionalized ILs, which help the TMA molecules to diffuse and adsorb onto the array surface and assist electron transfer. The formation mechanism of the mesoporous nanorod arrays was also discussed in detail.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...