Machine learning molecular dynamics for the simulation of infrared spectra†
Abstract
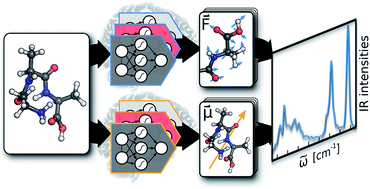
Machine learning has emerged as an invaluable tool in many research areas. In the present work, we harness this power to predict highly accurate molecular infrared spectra with unprecedented computational efficiency. To account for vibrational anharmonic and dynamical effects – typically neglected by conventional quantum chemistry approaches – we base our machine learning strategy on ab initio molecular dynamics simulations. While these simulations are usually extremely time consuming even for small molecules, we overcome these limitations by leveraging the power of a variety of machine learning techniques, not only accelerating simulations by several orders of magnitude, but also greatly extending the size of systems that can be treated. To this end, we develop a molecular dipole moment model based on environment dependent neural network charges and combine it with the neural network potential approach of Behler and Parrinello. Contrary to the prevalent big data philosophy, we are able to obtain very accurate machine learning models for the prediction of infrared spectra based on only a few hundreds of electronic structure reference points. This is made possible through the use of molecular forces during neural network potential training and the introduction of a fully automated sampling scheme. We demonstrate the power of our machine learning approach by applying it to model the infrared spectra of a methanol molecule, n-alkanes containing up to 200 atoms and the protonated alanine tripeptide, which at the same time represents the first application of machine learning techniques to simulate the dynamics of a peptide. In all of these case studies we find an excellent agreement between the infrared spectra predicted via machine learning models and the respective theoretical and experimental spectra.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...