An albumin-based tumor-targeted oxaliplatin prodrug with distinctly improved anticancer activity in vivo†
Abstract
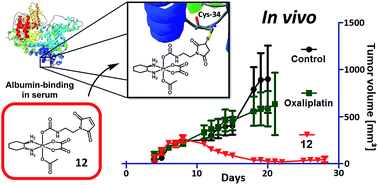
The design of targeted platinum(IV) prodrugs is a very promising approach to enhance the low selectivity of platinum(II) drugs towards cancerous tissue in order to reduce the impact on healthy tissue and, consequently, the often severe side-effects. Herein, we report a set of mono-functionalized cis- and oxaliplatin-based platinum(IV) complexes bearing a maleimide moiety, which allows selective binding to serum albumin in the bloodstream. This leads not only to a prolonged plasma half-life by avoidance of fast renal clearance, but also to preferential accumulation of the drug in the tumor tissue due to the EPR-effect. Additionally, analogous succinimide-functionalized derivatives were prepared to verify the influence of the maleimide moiety. First experiments showed that all the maleimide compounds are stable and also possess good albumin-binding properties in whole serum. Further analytical studies on in vivo samples proved the highly increased plasma half-life, as well as tumor accumulation of the maleimide-functionalized substances. In vivo antitumor experiments with CT-26-bearing mice showed that, in contrast to the cisplatin derivatives, the oxaliplatin-based complexes had exceptionally better activity than the free drug resulting in the cure of the majority of treated mice. Subsequent analysis suggested that a distinctly faster reduction as well as reduced tumor accumulation of the cisplatin derivative might explain the worse performance compared to the oxaliplatin(IV) complexes. Taken together, a novel lead platinum(IV) complex with outstanding antitumor activity is presented, which will now be further developed towards clinical phase I trials.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...