Evaluation of the protective effects of 13 traditional Chinese medicine compounds on ionizing radiation injury: bupleurum, shenmai, and breviscapine as candidate radioprotectors
Abstract
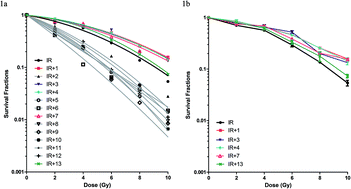
Background: Drugs are being sought that are effective as radioprotection for use in both planned and unplanned radiation exposure. Traditional Chinese medicines have been used successfully for the treatment of free radical-mediated diseases and therefore we expected that exploring such agents could yield an effective radioprotector. We therefore evaluated the radioprotective effects of 13 traditional Chinese medicine compounds (TCMCs) against ionizing radiation damage. Materials and methods: TCMCs were tested in vitro on human kidney 293T cells treated with 0, 2, 4, 6, 8 or 10 Gy irradiation for their ability to promote cell survival. Mice were subjected to a sub-lethal (4 Gy), lethal (7 Gy) or supra-lethal (13 Gy) dose of total-body irradiation (TBI) and TCMCs were tested for their ability to influence survival and hemopoietic function. Results: Of the 13 TCMCs tested, five including bupleurum, shenmai, and breviscapine, promoted survival of 293T cells. bupleurum, shenmai, and breviscapine also prolonged survival times of mice treated with supra-lethal and lethal TBI doses. As expected of an effective radioprotector, they also ameliorated bone marrow suppression, reducing the decrease in bone marrow cells after sub-lethal TBI, and they attenuated the TBI-induced reduction in granulocyte-macrophage colony-forming units. Conclusion: This investigation of TCMCs in vitro and in vivo identified bupleurum, shenmai, and breviscapine as having characteristics consistent with radioprotective agents. Further investigation to identify the bioactive components responsible for the radioprotective effect of these compounds is now required.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...