Synthesis, characterization, and thermal and surface properties of co- and terpolymers based on fluorinated α-methylstyrenes and styrene†
Abstract
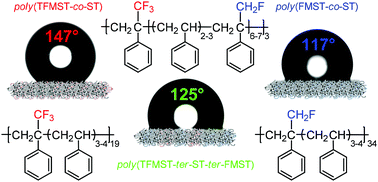
Conventional bulk radical co- and terpolymerizations of α-fluoromethylstyrene (FMST) or/and α-trifluoromethylstyrene (TFMST) with styrene (ST) initiated by α,α′-azobis(isobutyronitrile) (AIBN) are presented. The resulting poly(F-ST-co-ST) copolymers and poly(TFMST-ter-ST-ter-FMST) terpolymers were characterized by 1H, 19F and/or 13C NMR spectroscopy that evidenced the incorporation of fluorinated α-methylstyrenes and enabled the assessment of the molar percentages of base units (in copolymers, 10.2–49.7 mol% of FMST and 10.6–48.3 mol% of TFMST and in terpolymers, F-ST mol% ranging between 5.2–38.4 and 3.7– 14.5 for FMST and TFMST, respectively). The molecular weights were in the range of 1500–23 700 g mol−1, 1500–14 600 g mol−1 and 6900–10 900 g mol−1 for poly(FMST-co-ST) and poly(TFMST-co-ST) copolymers and poly(TFMST-ter-ST-ter-FMST) terpolymers, respectively. The bulkier CF3 group induced a slightly lower reactivity of the TFMST comonomer. From the extended Kelen–Tüdős (EK–T) linear method, the kinetics of the copolymerizations led to the determination of the reactivity ratios, ri, of both comonomers for each copolymerization system (rFMST = 0.08 ± 0.02 and rST = 0.72 ± 0.04, rTFMST = 0.00 and rST = 0.64 ± 0.01 at 70 °C), showing that F-ST monomers were less reactive than ST and retarded the rate of polymerization, and thus reduced the molecular weights. However, in the case of terpolymerizations where all three monomers were incorporated into polymeric chains, the retarding effects of F-STs were less noticeable, indicating that a termonomer induced copolymerization occurred. Finally, the thermal properties of these copolymers showed that the presence of fluorinated monomer units incorporated into the polystyrenic structure promoted an increase of the glass transition temperatures of the resulting copolymers up to 114 °C [poly(TFMST-co-ST) copolymer] and a slightly better thermal stability than that of polystyrene. Furthermore, the relationships between the surface structure of varied fluorinated copolymers and their wetting and oleophobic properties showed that below 80 mol% of styrene repeating units, the incorporation of 20–40 mol% of FMST or 10–20 mol% of TFMST in the copolymer structure caused a major change in the contact angle of the copolymers, reaching an unexpectedly high water contact angle of up to 147°.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...