Label-free colorimetric detection of tetracycline using analyte-responsive inverse-opal hydrogels based on molecular imprinting technology†
Abstract
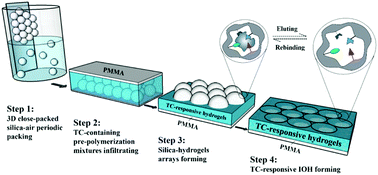
Novel analyte-responsive inverse-opal hydrogels (IOHs) based on molecular imprinting technology were fabricated to generate a highly selective and sensitive device for the colorimetric detection of tetracycline (TC). The TC-responsive IOHs were constructed by packing periodic silica–air arrays and then photo-polymerizing TC-containing hydrogels between the closely packed silica microspheres. Next, the original silica microspheres were etched, and the TC template molecules were eluted with the remaining hydrogel–air arrays. The abundant imprinted sites in the thin hydrogel walls specifically rebound TC via hydrogen bonds, leading to a periodic spacing change and a Bragg diffraction peak shift that converted the rebinding events into readable optical signals. The TC-responsive IOHs offered favorable linearity over four orders of magnitude (10−10–10−6 mol L−1) with a Bragg diffraction peak blue shift of approximately 43 nm. Excellent recognition selectivity for TC over its analog was also attained. Furthermore, the TC-responsive IOHs were successfully applied to detect TC in food samples of milk and meat, with high recoveries of 88.9–112.0% and 87.0–108.7%, respectively. Using TC as a model, the imprinted analyte-responsive IOHs show great potential as a rapid and cost-effective method for direct, label-free, and sensitive colorimetric measurements of trace pollutants in complicated samples.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...