Elucidating the biosynthetic pathways of volatile organic compounds in Mycobacterium tuberculosis through a computational approach†
Abstract
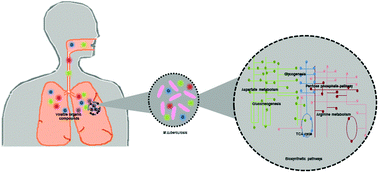
Microbial volatile organic compounds (VOCs) have gained prominence in the recent past for their potential use as disease markers. The discovery of microbial VOCs has benefited ‘difficult to detect’ diseases such as tuberculosis (TB). Few of the identified VOCs of Mycobacterium tuberculosis (Mtb) are currently being explored for their diagnostic potential. However, very little is known about the biosynthesis of these small lipophilic molecules. Here, we propose putative biosynthetic pathways in Mycobacterium tuberculosis for three VOCs, namely methyl nicotinate, methyl phenylacetate and methyl p-anisate, using computational approaches. In particular, we identify S-adenosyl methionine (SAM) transferases that play a crucial role in esterification of the acids to the final product. Our results provide important insights into the specificity of these pathways to Mtb species.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...