The effects of Lycium barbarum L. (L. barbarum) on cardiometabolic risk factors: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials†
Abstract
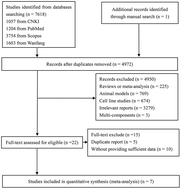
The effects of Lycium barbarum L. (L. barbarum) on the cardiometabolic risk factors from randomized controlled trials (RCTs) have shown inconsistent results. The present meta-analysis aimed to investigate the effects of L. barbarum supplementation on the cardiometabolic risk factors. A systematic literature search was performed in Chinese National Knowledge Infrastructure (CNKI), PubMed, Scopus, and Wanfang databases updated to March 2017. The mean changes in cardiometabolic risk factors were calculated as the weighted mean difference (WMD) using a random-effects model. Seven RCTs with a total of 548 subjects were included. The pooled estimate showed that L. barbarum intervention significantly reduced the fasting glucose concentrations (−0.36 mmol L−1/−6.5 mg dL−1; 95% confident interval (CI): −0.62, −0.10 mmol L−1/−11.3, −1.8 mg dL−1). In addition, L. barbarum supplementation marginally reduced the concentrations of total cholesterol (TC) (−0.30 mmol L−1/−11.6 mg dL−1; 95% CI: −0.75, 0.15 mmol L−1/−29.0, 5.8 mg dL−1; P = 0.189) and triglyceride (TG) (−0.20 mmol L−1/−17.7 mg dL−1; 95% CI: −0.46, 0.05 mmol L−1/−40.7, 4.4 mg dL−1; P = 0.122), but the summary estimates did not reach statistical significance. No benefit was found in relation to bodyweight and blood pressure. The present meta-analysis provides some evidence that supplemental L. barbarum might have favourable effect on glucose control.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...