Sludge concentration, shear rate and nanoparticle size determine silver nanoparticle removal during wastewater treatment†
Abstract
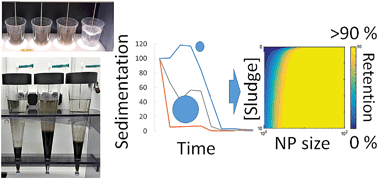
Wastewater treatment (WWT) is generally efficient in removing nanoparticles (NPs) from sewage effluent, but the variety in removal rates has not yet been explained. WWT parameters such as the activated sludge (AS) concentration, shear rate and ionic strength were varied in kinetic batch attachment and sedimentation studies using silver NPs having nominal 20 or 80 nm sizes and citrate or PEG coatings. The fitted attachment and detachment rate constants and the resulting distribution ratios at steady state varied with WWT process parameters, but most notably with the NP size, which was also found to influence the settling rates most. The NP coating molecules had a limited or no effect. A meta-analysis of literature distribution ratios (attached/detached concentration) of NPs composed of Ag and other materials showed the NP (aggregate) size as the only significant parameter. However, while the distribution ratio of silver NPs to AS increased linearly with AS concentration, the final effect of NP effluent concentrations is partly offset by decreased sedimentation rates. The results thus confirm that a WWT process is efficient in removing NPs from wastewater, but relatively small (<20 nm) non-aggregated NPs are somewhat more likely to exit a WWT process via the effluent into aquatic compartments compared to relatively larger NPs, which nearly entirely leave the WWT plants with the AS towards soils, incineration plants or landfills.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...