Membranes for artificial photosynthesis
Abstract
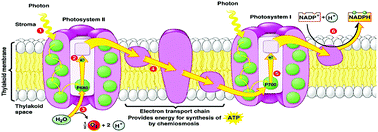
Membrane-based architectures enable optimization of charge transport and electrochemical potential gradients in artificial photosynthesis. Spatial integration of the membrane-bound components reduces the impact of charge recombination and can reduce electrical resistances associated with ionic and electronic transport processes. In addition to eliminating the need for external electrical circuits, a membrane-based architecture also ensures separation of energetic products, thereby preventing the formation of potentially dangerous fuel/oxidant mixtures. Membrane-based structures may also be coupled with other devices, such as perovskite-based solar cells, to further benefit solar fuel production. This review discusses the key roles that various different types of membranes play in artificial photosynthetic systems.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...