Highly efficient hydrogen evolution from seawater by a low-cost and stable CoMoP@C electrocatalyst superior to Pt/C†
Abstract
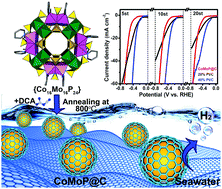
The hydrogen evolution reaction (HER) based on water electrolysis is a promising strategy for hydrogen energy production, in which the key point is seeking low-cost, high efficiency and stable electrocatalysts. Currently, the most efficient electrocatalysts for the HER are Pt-based catalysts (especially commercial Pt/C), but the low abundance and high cost of Pt hinder their widespread application. Herein, we demonstrate that a cobalt molybdenum phosphide nanocrystal coated by a few-layer N-doped carbon shell (CoMoP@C) is an excellent substitute for the HER. CoMoP@C is prepared by a one-step pyrolysis method on a large scale with polyoxometalate (POM) as a molecular platform. The catalytic activity of CoMoP@C is close to that of commercial 20% Pt/C under pH = 0–1 conditions and superior to that of 20% Pt/C under pH = 2–14 conditions at high overpotential (e.g. η > 240 mV at pH = 2.2). In real seawater, CoMoP@C exhibits stable HER performance with a high Faradaic efficiency (FE) of 92.5%, while the HER activity of 20% Pt/C dramatically decreases after 4 h. The remarkable HER performance of CoMoP@C should be attributed to the low free energy of H on the central CoMoP crystalline core and the multiple functions of the outer N-doped C shell (especially the strong H+ absorption behavior). This work may provide new options for the design and preparation of promising HER electrocatalysts superior to Pt/C, which can be used directly in seawater.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...