Lignocellulose fermentation and residual solids characterization for senescent switchgrass fermentation by Clostridium thermocellum in the presence and absence of continuous in situ ball-milling†
Abstract
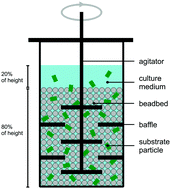
Milling during lignocellulosic fermentation, henceforth referred to as cotreatment, is investigated as an alternative to thermochemical pretreatment as a means of enhancing biological solubilization of lignocellulose. We investigate the impact of milling on soluble substrate fermentation by Clostridium thermocellum with comparison to yeast, document solubilization for fermentation of senescent switchgrass with and without ball milling, and characterize residual solids. Soluble substrate fermentation by C. thermocellum proceeded readily in the presence of continuous ball milling but was completely arrested for yeast. Total fractional carbohydrate solubilization achieved after fermentation of senescent switchgrass by C. thermocellum for 5 days was 0.45 without cotreatment or pretreatment, 0.81 with hydrothermal pretreatment (200 °C, 15 minutes, severity 4.2), and 0.88 with cotreatment. Acetate and ethanol were the main fermentation products, and were produced at similar ratios with and without cotreatment. Analysis of solid residues was undertaken using molecular beam mass spectrometry (PyMBMS) and solid-state nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy (NMR) in order to provide insight into changes in plant cell walls during processing via various modes. The structure of lignin present in residual solids remaining after fermentation with cotreatment appeared to change little, with substantially greater changes observed for hydrothermal pretreatment – particularly with respect to formation of C–C bonds. The observation of high solubilization with little apparent modification of the residue is consistent with cotreatment enhancing solubilization primarily by increasing the access of saccharolytic enzymes to the feedstock, and C. thermocellum being able to attack all the major linkages in cellulosic biomass provided that these linkages are accessible.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...