Catalytic hydrogenation of CO2 to methane over supported Pd, Rh and Ni catalysts†
Abstract
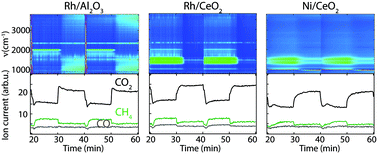
As a step in production of so-called electrofuels, ambient pressure CO2 hydrogenation has been investigated over different catalytic model systems based on metal particles (Pd, Rh and Ni) supported on various metal oxides (SiO2, Al2O3 and CeO2) and aluminosilicates (ZSM-5 and MCM-41) at different specific reactant ratios and temperatures between 150 and 450 °C. Catalytic activity and selectivity measurements in a flow reactor show that the highest CO2 conversion towards methane is obtained for the Rh/Al2O3 and Rh/CeO2 catalysts, followed by Ni/CeO2. Generally, the results suggest that both the support material and reaction conditions play an important role in the hydrogenation process. Further, in situ diffusive reflectance infrared Fourier transform spectroscopy reveals the intermediate species during transient CO2 hydrogenation over the Rh and Ni containing catalysts. Adsorption and dissociation of CO2 occurs over the Rh/Al2O3 catalyst in the presence of H2, resulting in the formation of linear Rh–CO species, while formates and carbonates are formed over the Rh/CeO2 and Ni/CeO2 catalysts, likely at the metal–support interface.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...