Validation of a membrane touch biosensor for the qualitative detection of IgG class antibodies to herpes simplex virus type 2
Abstract
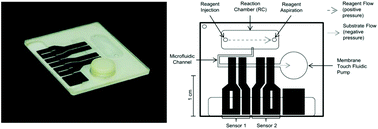
A novel type of biosensor was assessed for application to the qualitative determination of circulating antibodies to herpes simplex virus type 2 (HSV-2). The device utilises a high activity HSV-2 type specific gG2 antigen for antibody capture and commercially available ELISA reagents. The study compares the diagnostic performance of a prototype HSV-2 biochip to well-established in vitro tests routinely applied in clinical procedures. A panel of human serum samples (n = 60) previously characterised for HSV-2 serological status using the DiaSorin LIAISON® HSV-2 chemiluminescent immunoassay were assayed on the HSV-2 biochip and the Focus Diagnostics HerpeSelect® 2 ELISA IgG kit to determine concordance with the predicate test method. Sensitivity and specificity of the HSV-2 biochip were found comparable to both the DiaSorin and Focus test methods. Sample index values calculated from the immunoassay response of the biochip's coulometric sensors indicated a high degree of linear correlation of the dataset with the corresponding index values from the DiaSorin LIAISON® test (r2 0.8799) and Focus HerpeSelect® test (r2 0.8794). The HSV-2 biochip demonstrated excellent diagnostic performance in qualitative and semi-quantitative measurements, matching closely the performance of two diagnostic industry standard predicate methods.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...