FTIR imaging of the molecular burden around Aβ deposits in an early-stage 3-Tg-APP-PSP1-TAU mouse model of Alzheimer's disease
Abstract
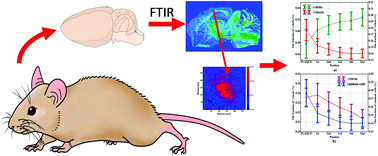
Alzheimer's disease is one of the major causes of dementia in the elderly. The disease is caused by the misfolding of water soluble alpha-helical proteins, which leads to the accumulation of β-sheets in the form of amyloid plaques, which can subsequently affect surrounding tissue areas by oxidative stress neurotoxicity. The aim of the present study was to design a novel methodology to analyze the extent to the neuronal burden around protein-rich Aβ plaques suspected to affect molecular components by oxidative stress induced by inflammatory states. To do so, sagittal brain tissue sections from triple transgenic APPxPSP1xTAU mice were used to carry high magnification FTIR-FPA bench-top chemical imaging. The study used the combination of chemometric procedures involving spectral curve fitting and image processing to study the molecular changes occurring around the plaques. The study shows the performance of the approach by demonstrating its usefulness to co-localize molecular changes to different areas around the plaques. The results, although very preliminary, point to the strong interplay between the distance from the plaque and co-accumulation of molecular components indicative of inflammatory states.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...