Investigations of the genotoxic properties of two synthetic cathinones (3-MMC, 4-MEC) which are used as psychoactive drugs
Abstract
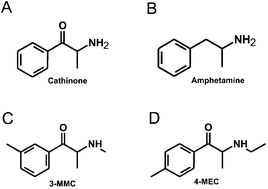
Synthetic cathinones (SCAs) are consumed worldwide as psychostimulants and are increasingly marketed as surrogates of classical illicit drugs via the internet. The genotoxic properties of most of these drugs have not been investigated. Results of earlier studies show that amphetamines which are structurally closely related to these compounds cause damage to the genetic material. Therefore, we tested the genotoxic properties of two widely consumed SCAs, namely, 3-MMC (2-(methylamino)-1-(3-methylphenyl) propan-1-one) and 4-MEC (2-(ethylamino)-1-(4-methylphenyl) propan-1-one) in a panel of genotoxicity tests. We found no evidence for induction of gene mutations in Salmonella/microsome assays, but both drugs caused positive results in the single cell gel electrophoresis (SCGE) assay which detects single and double strand breaks of DNA in a human derived buccal cell line (TR146). 3-MMC induced similar effects as 4-MEC and also caused significant induction of micronuclei which are formed as a consequence of structural and chromosomal aberrations. Negative results obtained in SCGE experiments with lesion specific enzymes (FPG and Endo III) show that these drugs do not cause oxidative damage of DNA. However, moderate induction of TBARS (which leads to the formation of DNA-reactive substances) was observed with 4-MEC, indicating that the drug causes lipid peroxidation while no clear effect was detected with 3-MMC. Results obtained with liver homogenate in SCGE-experiments show that phase I enzymes do not lead to the formation of DNA reactive metabolites. Taken together, our findings indicate that consumption of certain SCAs may cause adverse health effects in users as a consequence of damage to the genetic material.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...