A TCO-free Prussian blue-based redox-flow electrochromic window
Abstract
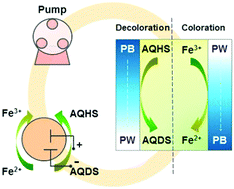
A TCO (transparent conductive oxide)-free redox-flow electrochromic window (RFEW) with considerably improved performance is demonstrated. The new RFEW employs Prussian blue (PB)/Prussian white (PW) as the electrochromic (EC) material, in which the decoloration/coloration is achieved by the redox targeting reactions of anthraquinone-2,6-disulfonate (AQDS) and FeCl3 with PB/PW, respectively. These redox molecules are electrochemically oxidized/reduced in an external stack cell and circulated through the window cavity. Hence, the costly TCO glass, indispensable in conventional EC windows, becomes redundant in RFEWs. Owing to the fast charge transfer kinetics of AQDS and Fe3+, the RFEW design investigated in this study presents substantially reduced response time. For a window with a size exceeding 100 cm2, coloration/decoloration switching with a change in absorbance by more than 80% is achieved within approximately 2 min. The static and dynamic optical characteristics of the window pane and the electrochemical behavior of the stack cell were examined in detail to understand the operation of the RFEW.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...