Electric field induced reversible and irreversible photoluminescence responses in methylammonium lead iodide perovskite†
Abstract
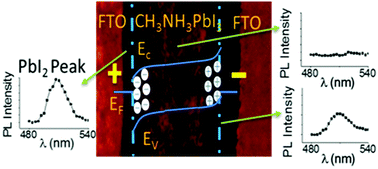
Electric field induced effects have attracted considerable interest in the field of perovskite materials and solar cells because they are closely related to the performance and stability. In this work, we visualize and characterize the electric field induced effects in laterally structured Au/FTO/CH3NH3PbI3/FTO/Au samples via photoluminescence optical microscopy, in situ time-correlated single photon counting measurements and scanning electron microscopy. Both irreversible and reversible responses are observed under different electric fields and humidity conditions. Firstly, the irreversible response near both electrodes includes permanent photoluminescence quenching and morphology changes. Such changes are observed when the applied field is larger than a nominal value, which depends on the humidity conditions. The irreversible change is a result of perovskite decomposition, which is indicated by the appearance of a PbI2 peak in the localized photoluminescence spectrum. We show that this moisture-assisted electric field induced decomposition can be minimized by encapsulation. Secondly, a reversible response near the anode observed under a weak electric field, which is characterized by photoluminescence quenching and a reduced lifetime with negligible morphology change, is attributed to the migration and accumulation of mobile ions. The dominant mobile species is ascribed to be iodide ions by mobility calculations. Thirdly, a slowdown of the irreversible response, i.e., decomposition within the bulk of the perovskite and away from the electrodes, is observed. This is because of the negative feedback between perovskite decomposition and ion accumulation, which offsets the field induced effect in the perovskite bulk. This work demonstrates the effective use of photoluminescence microscopy revealing different mechanisms behind the observed instability of perovskite devices under different bias and moisture conditions that cause either reversible or irreversible changes.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...