Wetting properties and SERS applications of ZnO/Ag nanowire arrays patterned by a screen printing method†
Abstract
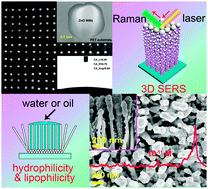
Three-dimensional (3D) ZnO/Ag nanowire arrays (NWA) SERS substrates are fabricated by a screen-printing technique. The preparation of patterned ZnO NWA involves a two-step growth process. The ZnO nanoparticles-based ink is prepared and printed as seed layers, which are used as templates to fabricate patterned ZnO NWA via a hydrothermal method. During the screen printing process, the patterns of ZnO NWA are controlled by printing plates. The as-obtained NWA with uniform morphology was fabricated at 90 °C and exhibits hydrophilic and lipophilic properties. Subsequently, the sensitive 3D SERS substrates are fabricated through deposition of Ag nanoparticles (NPs) onto the surface of patterned ZnO NWA by magnetron sputtering. The detection limit of Malachite green (MG) can achieve 10−12 M with an enhancement factor of about 2.5 × 1010. Combined with the sensitivity and uniformity, the ZnO/Ag NWA is applied for the quick detection of low concentrations of molecules related to food safety, such as amoxicillin.
 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...