Ultrabroad near-infrared photoluminescence from bismuth doped CsPbI3: polaronic defects vs. bismuth active centers†
Abstract
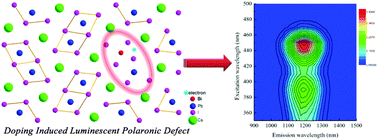
Bismuth doped materials with near infrared (NIR) photoluminescence (PL) have recently attracted tremendous attention because of their great potential for photonic and optoelectronic devices that could find broad applications in modern optical telecommunications. However, the mechanistic studies of the NIR PL from these materials still significantly lag behind, which imposes substantial limitations in rationally discovering and designing new materials. In this contribution, we investigated the optical and structural properties of Bi doped CsPbI3 using a diverse range of experimental techniques. We proved that the observed ultrabroad NIR PL with lifetimes of tens of microseconds is not connected with a single-ion Bi active center. For the first time, we proposed a polaron model to rationally explain the observed PL from Bi doped CsPbI3. Finally, we demonstrate the first observation of NIR PL from nanowires among the Bi doped luminescent materials. The experimental results reported here not only deepen the understanding of NIR PL mechanisms in Bi doped materials, but also introduce a new family of solution-processed nanostructures operating in the NIR, which may stimulate further research in exploiting this technique to design a broad range of photonic and optoelectronic devices.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...