Tuning the properties of injectable poly(oligoethylene glycol methacrylate) hydrogels by controlling precursor polymer molecular weight†
Abstract
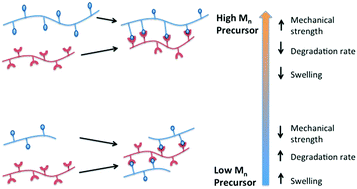
Tuning the properties of in situ-gelling injectable hydrogels based on synthetic polymers typically involves changing the chemistry of polymer backbones or the density of reactive functional groups on precursor polymers. Herein, we describe injectable, hydrazone crosslinked hydrogels based on well-defined poly(oligoethylene glycol methacrylate) (POEGMA) precursors prepared via reversible addition–fragmentation chain transfer (RAFT). These hydrogels have different molecular weights but similar functional group content, enabling engineering of hydrogel properties without substantially changing the chemistry of the precursor polymer. Specifically, although the number of functional crosslinks formed in each gel was found to be equivalent, hydrogels prepared with higher molecular weight precursor polymers showed faster gelation times, higher compressive and shear moduli, slower degradation, and less swelling than gels prepared with lower molecular weight precursor polymers. Thus, this approach is particularly attractive in cases in which separating the effects of physical and chemical changes to gel substrates is critical to understanding or controlling underlying biological interactions.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...