Blood clot initiation by mesoporous silica nanoparticles: dependence on pore size or particle size?
Abstract
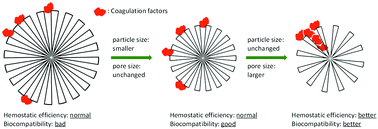
Mesoporous silica nanoparticles (MSNs) with controllable pore size and particle size were prepared using a vesicle-organic template method. Transmission electron microscopy (TEM), nitrogen adsorption measurements, X-ray diffraction (XRD) and Fourier transform infrared (FTIR) spectra were used to characterize the coagulation-promoting surface chemistry, topologies and porous structure of the MSNs. The clotting blood tests (CBTs) showed that the pore sizes of the MSNs varying from 5 nm to 15 nm greatly affected the blood clot rate of rabbit plasma, while variation of the particle size from 60 nm to 220 nm had little influence on coagulation. Associated with the blood coagulation factor XII (FXII) tests, it could be inferred that the accessibility and diffusion of clotting were mainly dependent on the pore size of the MSNs. Proper pore size could readily promote the blood proteins to contact the huge interior surfaces of the MSNs and then initiate the quick blood clot. Furthermore, the perfect biocompatibility of the MSNs was achieved through a CCK-8 and cellular uptake study, indicating that cell viability could be promoted by MSNs and MSNs with larger pore size showed better biocompatibility. Rapid hemostasis in rabbit femoral artery injury testified the superb hemostatic efficiency of the MSNs. We demonstrated that MSNs with a pore size of 15 nm showed the best hemostatic efficiency and it would be probably an optimal candidate for the first aid of hemorrhage in the field or pre-hospital.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...