Preparation and characterization of a biodegradable polyurethane hydrogel and the hybrid gel with soy protein for 3D cell-laden bioprinting†
Abstract
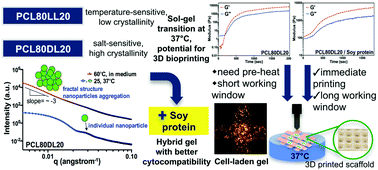
3D printing shows great potential for fabricating customized scaffolds for tissue regeneration. Using hydrogel as a bioink for cell printing provides a biological platform for basic research and potential medical treatments. In this study, a waterborne poly(ε-caprolactone) (PCL)-based biodegradable polyurethane (PU) with a soft segment replaced with 20 mol% of poly(L-lactide) (PLLA) diol or poly (D,L-lactide) (PDLLA) diol was prepared. These two PUs formed compact packing structures at temperatures ≥37 °C. They responded differently to temperature changes and the presence of electrolytes because of the difference in the free volume. With their thermal-responsive properties, both PU dispersions could form a gel in 3 min with the gel modulus reaching about 6–8 kPa after 30 min. To enhance the structural integrity during layer-by-layer deposition, the hybrid hydrogel of PU and soy protein isolate (PU/SPI hybrid) was further developed. The PU/SPI hybrid dispersion could undergo rapid gelation at 37 °C with the modulus reaching 130 Pa in 1 min. Moreover, the PU/SPI hybrid gel was readily blended with cells and printed at 37 °C without preheating. Neural stem cells (NSCs) were embedded in the hydrogels and analyzed for cell viability, metabolism, proliferation, and gene expression of neural-related markers. Cells cultured in the PU/SPI hybrid construct had better survival and proliferation than those in the PU gel. The PU/SPI hybrid ink may provide unique rheological properties for direct cell/tissue printing at 37 °C and a biomimetic microenvironment for cell survival, growth, and differentiation.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...