The dual function of Cu-doped TiO2 coatings on titanium for application in percutaneous implants
Abstract
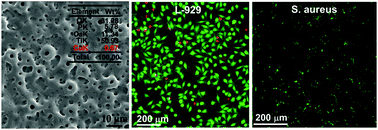
To endow percutaneous implants with improved skin integration and antibacterial activity, microporous TiO2 coatings doped with different doses of Cu2+ (0–1.93 wt%) were directly fabricated on Ti via micro-arc oxidation (MAO). The structures of coatings were investigated; the adhesion, proliferation, phenotype, differentiation and extracellular collagen secretion of fibroblasts, as well as the response of Staphylococcus aureus (S. aureus), were also investigated. The obtained results show that microporous TiO2 coatings all consist of antase and rutile, and incorporation of Cu2+ almost does not alter the phase component, surface roughness and topography of coating. Cu2+ facilitates the fibroblasts to switch to fibrotic phenotype and differentiate to myofibroblasts by enhancing the production of intracellular specific protein contents (connective tissue growth factor (CTGF) and alpha smooth muscle action (α-SMA)). Compared to Ti, the adhesion and proliferation of fibroblasts can be significantly enhanced on the TiO2 coating with 0.67 wt% Cu, while greatly inhibited with 1.93 wt% Cu. The difference should be due to the compromise between the positive effectiveness and the cytotoxicity of Cu2+. Cu2+-doped TiO2 coatings show good antibacterial properties, including contact-killing and release-killing of S. aureus, and these properties are positively related to the dose of Cu2+ in the coatings.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...