Photon energy storage materials with high energy densities based on diacetylene–azobenzene derivatives†
Abstract
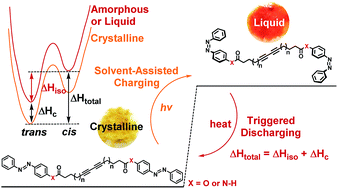
Photocontrolled self-assembly of molecules has been utilized to change the physical properties of organic materials for various applications, while photon energy storage materials that incorporate photochromic molecules such as azobenzenes have been recognized as another highly attractive class of materials that convert and store photon energy in the strained chemical bonds. Herein, we demonstrate the photocontrolled self-assembly and disassembly of photon energy storage materials based on new diacetylene derivatives with azobenzene moieties and with varied alkyl spacers and linkers. We developed a series of symmetric diacetylenes and polydiacetylenes and obtained high energy-density materials that can store up to 176.2 kJ mol−1 (or 200.2 kJ mol−1, if completely charged); more than double that of pristine azobenzene. The extra energy storage in the materials in addition to the isomerization enthalpy of azobenzene units is enabled by the different phase of materials in the ground state (crystalline solid) and in metastable state (amorphous solid/liquid). It is notable that the phase change characteristic of organic materials can be a parameter to consider in terms of designing high energy density photon energy storage materials.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...