Bifunctional CoP and CoN porous nanocatalysts derived from ZIF-67 in situ grown on nanowire photoelectrodes for efficient photoelectrochemical water splitting and CO2 reduction†
Abstract
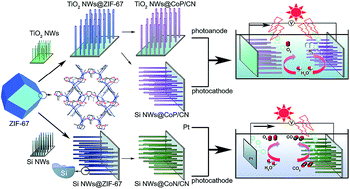
To develop highly efficient and non-noble metal catalysts in solar-driven photoelectrochemical cells for water splitting and CO2 reduction is a tremendous challenge but there is a strong desire to accomplish it. Herein, CoP- and CoN-based porous nanocatalysts, which were in situ transformed from Co-based zeolitic imidazolate framework (ZIF-67), are reported as efficient co-catalysts for photoelectrochemical water splitting and CO2 reduction. The CoP wrapped with N-doped carbon (CoP/CN) nano-electrocatalysts, with high catalytic activity and stability for both the hydrogen (HER) and oxygen (OER) evolution reactions in situ coated with TiO2 nanowires (TiO2 NWs@CoP/CN), and the p-type Si nanowires (Si NWs@CoP/CN) strikingly promoted photoelectrochemical water splitting by serving as a photoanode and a photocathode, respectively, whereas CoN wrapped with N-doped carbon (CoN/CN) nanocatalysts presented excellent electrocatalytic activity towards CO2 reduction with a low onset potential, high selectivity, and good stability. It can be noted that CoN/CN catalysts-covered p-type Si nanowires (Si NWs@CoN/CN) also displayed high photoelectrochemical performance for CO2 reduction. The superior photoelectrochemical catalytic properties can be ascribed to the synergetic effect of the porous N-doped carbon network inherited from ZIF-67 and wrapped CoP or CoN nanoparticles as well as the superior interface achieved via the in situ growth method.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...