Binding TiO2-B nanosheets with N-doped carbon enables highly durable anodes for lithium-ion batteries†
Abstract
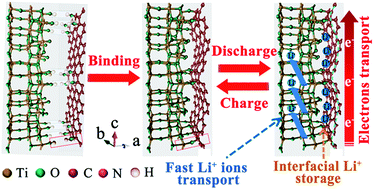
An effective strategy of binding TiO2-B nanosheets with N-doped carbon is developed to construct highly stable TiO2-B (001)|carbon interfaces with enhanced electronic conductivity and Li-uptake capability. The interfaces provide not only additional interfacial lithium-storage capability but also highly conductive pathways for the fast transport of electrons and lithium ions. The hybrid as an anode for lithium-ion batteries exhibits a safe operating potential window of ∼1.5 V, superior rate capability with 180 mA h g−1 at 6 A g−1, and ultra-long cycle life of more than 2000 cycles, holding great promise for safe and high-power energy storage applications.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...