Saltwater as the energy source for low-cost, safe rechargeable batteries†
Abstract
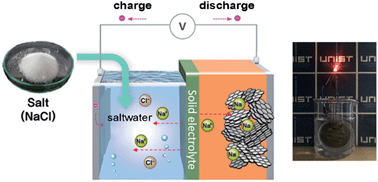
The effective use of electricity from renewable sources requires large-scale stationary electrical energy storage (EES) systems with rechargeable high-energy-density, low-cost batteries. We report a rechargeable saltwater battery using NaCl (aq.) as the energy source (catholyte). The battery is operated by evolution/reduction reactions of gases (mostly O2, with possible Cl2) in saltwater at the cathode, along with reduction/oxidation reactions of Na/Na+ at the anode. The use of saltwater and the Na-metal-free anode enables high safety and low cost, as well as control of cell voltage and energy density by changing the salt concentration. The battery with a hard carbon anode and 5 M saltwater demonstrated excellent cycling stability with a high discharge capacity of 296 mA h ghard carbon−1 and a coulombic efficiency of 98% over 50 cycles. Compared with other battery types, it offers greatly reduced energy cost and relatively low power cost when used in EES systems.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...