Effects of flux synthesis on SrNbO2N particles for photoelectrochemical water splitting†
Abstract
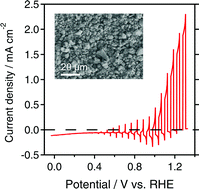
An investigation was carried out on the effects of using a flux during the fabrication of SrNbO2N particles on the photoelectrochemical (PEC) properties of CoPi/SrNbO2N/Nb/Ti photoanodes prepared by a particle transfer method. The type of flux and the synthesis conditions were found to affect the morphology and crystallinity of oxide precursors and subsequently nitrided SrNbO2N. By a suitable choice of flux synthesis conditions, the PEC performance of the photoanodes could be improved. Oxide precursors treated with a NaI flux were solid solutions of NaNbO3 and Sr4Nb2O9, and had a perovskite-type structure. When the precursors were first pre-calcined, larger secondary SrNbO2N particles with a higher degree of crystallinity were obtained. As a result, a photocurrent density of 1.5 mA cm−2 at 1.23 VRHE was achieved under simulated sunlight (AM 1.5G) in an alkaline solution (pH 13).


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...