One-step synthesis of a silicon/hematite@carbon hybrid nanosheet/silicon sandwich-like composite as an anode material for Li-ion batteries†
Abstract
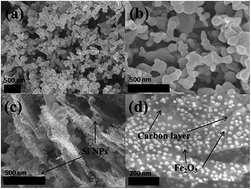
Silicon and hematite, both important functional materials with high theoretical capacity, have been intensively investigated separately for application as anode materials in lithium ion batteries (LIBs). The main challenges associated with these anode materials are their low electronic conductivity and structural degradation caused by large volume expansion during cycling, which are not tolerable for future LIBs with high energy density and large power output. Active particles anchored on a porous conductive skeleton are widely used for improving the electrochemical performance of silicon as well as that of hematite. Herein, we develop a novel-structured carbon–silicon–hematite anode material via a single-step technique that addresses these problems. In the resultant architecture, silicon nanoparticles are sandwiched between the iron-oxide-embedded porous carbon sheets. The flexible and conductive carbon sheets improve the conductivity and accommodate the volume changes of the embedded hematite and silicon nanoparticles, and thus maintain the structural and electrical integrity. Meanwhile, the void space between the carbon layers leaves enough room for the expansion and contraction of silicon during the lithiation and delithiation processes. High capacity (∼1980 mA h g−1 at 750 mA g−1) and long cycle life (250 cycles) have been achieved for this sandwich-like carbon–silicon–hematite electrode.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...