Enzymatically activated emulsions stabilised by interfacial nanofibre networks†
Abstract
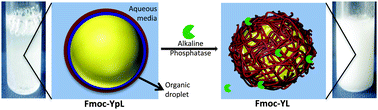
We report on-demand formation of emulsions stabilised by interfacial nanoscale networks. These are formed through biocatalytic dephosphorylation and self-assembly of Fmoc(9-fluorenylmethoxycarbonyl)dipeptide amphiphiles in aqueous/organic mixtures. This is achieved by using alkaline phosphatase which transforms surfactant-like phosphorylated precursors into self-assembling aromatic peptide amphiphiles (Fmoc-tyrosine-leucine, Fmoc-YL) that form nanofibrous networks. In biphasic organic/aqueous systems, these networks form preferentially at the interface thus providing a means of emulsion stabilisation. We demonstrate on-demand emulsification by enzyme addition, even after storage of the biphasic mixture for several weeks. Experimental (Fluorescence, FTIR spectroscopy, fluorescence microscopy, electron microscopy, atomic force microscopy) and computational techniques (atomistic molecular dynamics) are used to characterise the interfacial self-assembly process.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...