Into the polymer brush regime through the “grafting-to” method: densely polymer-grafted rodlike viruses with an unusual nematic liquid crystal behavior†
Abstract
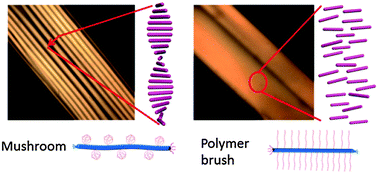
The current work reports an intriguing discovery of how the force exerted on protein complexes like filamentous viruses by the strong interchain repulsion of polymer brushes can induce subtle changes of the constituent subunits at the molecular scale. Such changes transform into the macroscopic rearrangement of the chiral ordering of the rodlike virus in three dimensions. For this, a straightforward “grafting-to” PEGylation method has been developed to densely graft a filamentous virus with poly(ethylene glycol) (PEG). The grafting density is so high that PEG is in the polymer brush regime, resulting in straight and thick rodlike particles with a thin viral backbone. Scission of the densely PEGylated viruses into fragments was observed due to the steric repulsion of the PEG brush, as facilitated by adsorption onto a mica surface. The high grafting density of PEG endows the virus with an isotropic–nematic (I–N) liquid crystal (LC) phase transition that is independent of the ionic strength and the densely PEGylated viruses enter into the nematic LC phase at much lower virus concentrations. Most importantly, while the intact virus and the one grafted with PEG of low grafting density can form a chiral nematic LC phase, the densely PEGylated viruses only form a pure nematic LC phase. This can be traced back to the secondary to tertiary structural change of the major coat protein of the virus, driven by the steric repulsion of the PEG brush. Quantitative parameters characterising the conformation of the grafted PEG derived from the grafting density or the I–N LC transition are elegantly consistent with the theoretical prediction.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...