A NIR dye with high-performance n-type semiconducting properties†
Abstract
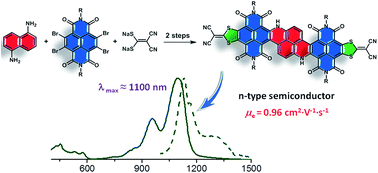
A novel hetero-polycyclic aromatic compound manifesting strong near-infrared (NIR) absorption as well as high-performance n-type semiconducting properties is developed. With an exceptionally low LUMO level at −4.7 eV, this NIR dye (λmax ≈ 1100 nm, ε ≈ 105 mol−1 L cm−1) exhibits adequate stability under ambient conditions, with electron mobility up to 0.96 cm2 V−1 s−1 measured in solution-processed organic field-effect transistors. A special metal-free C–C coupling serves as a pivotal step in constructing the polycyclic π-framework of this low-bandgap chromophore, by fusing an electron-deficient naphthalenediimide moiety with an electron-donating naphthalenediamine. Such a rare combination of extraordinary optical and semiconductive attributes is quite valuable for organic small molecules, and promising for unique applications in the opto-electronic field.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...