Phase transformations of novel CuxS nanostructures as highly efficient counter electrodes for stable and reproducible quantum dot-sensitized solar cells†
Abstract
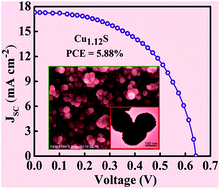
An ideal counter electrode (CE) that is cost-effective and has high electrocatalytic activity, high performance stability, and a simple fabrication process is essential for quantum dot-sensitized solar cells (QDSSCs). We report a facile one-step chemical bath deposition method for the growth of an L-cysteine-dependent CuxS thin film on a fluorine-doped tin oxide substrate, which was used as a highly efficient CE for QDSSCs. SEM images revealed that the surface morphology of CuxS changed from nanoplatelets to nanosheets to nanospheres to nanoflowers based on the concentration of L-cysteine. Also, the concentration of L-cysteine in the formation of CuxS thin films is expected to play an important role in determining the phase of CuxS thin films (Cu2S, Cu1.75S, Cu1.12S and CuS). QDSSCs based on Cu1.12S nanosphere CEs possess a high power conversion efficiency of 5.88%, which is much higher than those of QDSSCs based on Cu2S nanoplatelets (5.10%), Cu1.75S nanosheets (5.32%), CuS nanoflowers (4.88%) and Pt (1.36%) CEs. Electrochemical measurements revealed that a Cu1.12S nanosphere CE has better electrocatalytic activity, which increases the rate of reduction of polysulfide in comparison to those of Cu2S nanoplatelets, Cu1.75S nanosheets, CuS nanoflowers and Pt CEs. A QDSSC also displayed superior stability in an operational state for over 20 h, which is a major challenge for CuxS CEs.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...