Enhanced mechanical performance of cement nanocomposite reinforced with graphene oxide synthesized from mechanically milled graphite and its comparison with carbon nanotubes reinforced nanocomposite
Abstract
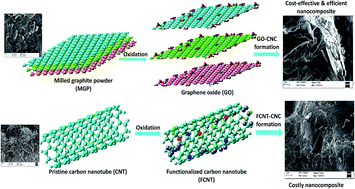
A highly reactive form of graphene oxide (GO) has been prepared from mechanically milled graphite powder (MGP) and characterized using different techniques such as FT-IR, SEM/EDS, TEM, XRD and AFM. Besides, functionalized carbon nanotubes (FCNT) were produced by oxidation of pristine carbon nanotubes (CNT) using acidic treatment. The cementitious nanocomposites (CNCs) containing different concentrations of GO or FCNT were evaluated for their compressive strength, tensile strength, microstructure and crystalline phase composition. The results obtained have shown that utilization of 1.00% of GO by wt of cement produces the highest enhancement in compressive strength by 77% whereas the incorporation of 0.25 wt% GO produces a tensile strength improvement of 37.5%. In contrast, 0.50 wt% FCNT improves the compressive strength by 58% with respect to control and an FCNT concentration of 0.25 wt% enhances the tensile strength up to 40%. The trends in mechanical behavior have been supported by the microstructural analysis and crystallization investigations of GO-CNCs and FCNT-CNCs. It is recommended that the higher improvement in compressive strength and comparable improvement in tensile strength by utilization of GO in comparison to FCNT makes it a potentially economical and efficient reinforcing material in cement-based matrices.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...