Near-infrared cyanine-based sensor for Fe3+ with high sensitivity: its intracellular imaging application in colorectal cancer cells†
Abstract
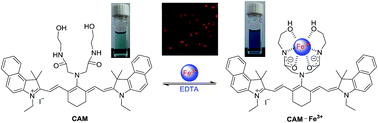
The ability to sense iron ions (Fe3+) has attracted considerable attention because of the crucial role that Fe3+ plays in a variety of vital cell functions. In this article, two novel near-infrared (NIR) cyanine-based compounds CAM and CAT bearing specific binding functional groups were developed for the detection of iron ions (Fe3+). Intriguingly, compared with CAT, only CAM with an N-(2-hydroxyethyl)acetamide group as the receptor can recognize the Fe3+ ion with high selectivity and sensitivity. The “naked-eye” color change from pea green to deep blue enables CAM to act as a highly efficient colorimetric sensor for the Fe3+ ion. Moreover, the unique NIR fluorescence response of CAM with Fe3+ was also observed in the presence of other competitive transition metal ions or cellular cations. Finally, CAM, with its excellent membrane permeability, was successfully applied for monitoring Fe3+ in colorectal cancer cells by fluorescence microscopy. This work offers a convenient colorimetric and fluorometric NIR Fe3+-selective probe based on the modification of typical tricarbocyanines, and cell imaging studies demonstrate that this sensor is capable of intracellular sensing of Fe3+ in living colorectal cancer cells, and eventually whole organisms.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...