Experimental research on the thermal decomposition of pentafluoroethane (HFC-125) extinguishing agent with n-heptane/air pool fire in confined space
Abstract
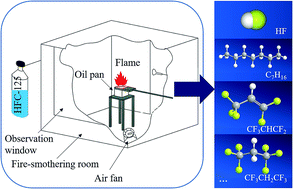
To discuss the production law of hazardous gases (e.g. hydrogen fluoride) during the interaction between a pentafluoroethane extinguishing agent and an n-heptane flame, we designed a simulation of experimental total flooding conditions that is highly similar to the actual total flooding automatic extinguishing conditions. In this study, a qualitative and quantitative analysis on the thermolysis gaseous products was performed through GC-MS and ion chromatography (IC) by studying the thermal decomposition characteristics of the interaction between a pentafluoroethane extinguishing agent and an n-heptane flame in a 1 m3 fire-smothering room under different fire sizes and interaction times. Research results demonstrated that the thermolysis gaseous products of the pentafluoroethane extinguishing agent and n-heptane flame include hydrogen fluoride (HF) and other organic gases, such as CF3CH![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) CF2 and CF3CH2CF3. The HF output was proportional to the fire size and interaction time. When the interaction time was controlled within 10 s, production of hazardous gases could be effectively reduced.
CF2 and CF3CH2CF3. The HF output was proportional to the fire size and interaction time. When the interaction time was controlled within 10 s, production of hazardous gases could be effectively reduced.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...