Ethanol thermal reduction synthesis of hierarchical MoO2–C hollow spheres with high rate performance for lithium ion batteries†
Abstract
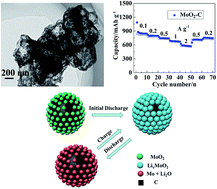
In the present work, we focus on the development of hierarchical MoO2–C hollow spheres with large reversible capacity and high rate capability in lithium ion batteries. The hierarchical MoO2–C hollow spheres assembled by MoO2 nanoparticles were initially synthesized successfully through ethanol thermal reduction method, followed by annealing process. Due to the synergistic effect between the assembled hierarchical hollow structure and the carbon coating, the sample exhibited excellent electrochemical properties as anode material for lithium-ion batteries. For example, a large reversible capacity of 763 mA h g−1 was obtained after 50 cycles at a current density of 0.2 A g−1. In addition, a large reversible capacity of 573 mA h g−1 can be remained when the current density reached at the high current density of 2 A g−1, indicating that the hierarchical MoO2–C hollow spheres electrode possess an outstanding rate performance.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...