Zero gap alkaline electrolysis cell design for renewable energy storage as hydrogen gas
Abstract
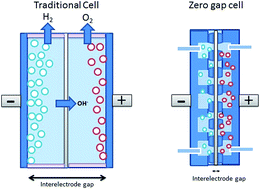
Zero gap alkaline electrolysers hold the key to cheap and efficient renewable energy storage via the production and distribution of hydrogen gas. A zero gap design, where porous electrodes are spacially separated only by the gas separator, allows the unique benefits of alkaline electrolysis to be combined with the high efficiencies currently only associated with the more expensive PEM set-up. This review covers the basics of alkaline electrolysis, and provides a detailed description of the advantages of employing a zero gap cell design over the traditional arrangement. A comparison with different types of zero gap cell designs currently seen in research is made, and a description of recent developments is presented. Finally, the current state of research into zero gap alkaline electrolysis is discussed, and pathways for future research identified. Zero gap alkaline electrolysis will allow excess renewable energy to be stored, transported and used on demand in a green and environmentally friendly manner as when the hydrogen is burnt or passed into a fuel cell it produces only water and energy.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...