Photochemical synthesis of CeO2 nanoscale particles using sodium azide as a photoactive material: effects of the annealing temperature and polyvinylpyrrolidone addition†
Abstract
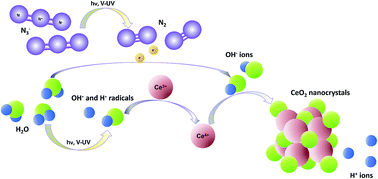
A novel and simple method for CeO2 nanoscale particle synthesis in aqueous solutions via a photochemical route is reported in this paper. To this end, CeCl3·7H2O or Ce(NO3)3·6H2O was used as a Ce precursor, while NaN3 was chosen as the photoactive compound. Synthesis was carried out without any surfactants or by using polyvinylpyrrolidone (PVP). The synthesized samples were subsequently thermally treated at different temperatures between 100 and 900 °C. XRD patterns and Raman spectra indicated that CeO2 samples possess the fluorite structure. TEM analysis revealed that synthesis without surfactants leads to formation of highly agglomerated particles, while adding PVP to the primary solution resulted in decreased agglomeration and reduced particle size. The particle size was calculated from XRD and Raman line broadening and confirmed by TEM analysis. The average crystallite size for the unheated samples prepared without surfactant was hardly radiation exposure dependent and varied from 6.5 to 8.9 nm. Even smaller particles (3.3–7.0 nm) were formed by using PVP. It turned out that an increase of the calcination temperature causes significant crystallite growth. A strong interaction between CeO2 nanoparticles and PVP was revealed by TG analysis. The UV/VIS absorption spectra showed a strong absorption below 400 nm (3.10 eV) with a well-defined absorption peak at around 295–320 nm. The estimated band gap (Eg) of the obtained nanoscale particles was in the range of 2.90–3.57 eV, i.e. the values are higher than that of a bulk CeO2 powder (Eg = 3.19 eV), except for the sample calcined at 900 °C.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...