Chiral separation by nonaqueous capillary electrophoresis using l-sorbose–boric acid complexes as chiral ion-pair selectors†
Abstract
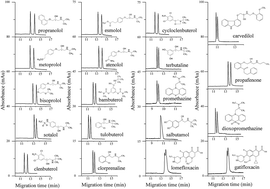
A chiral nonaqueous capillary electrophoresis (NACE) method using L-sorbose–boric acid complexes as the chiral ion-pair selectors was developed for enantioseparation of nineteen chiral analytes including eight β-blockers, seven β-agonists, two phenothiazines antihistamines, and two fluoroquinolone antibiotics. The effects of L-sorbose and boric acid concentrations, triethylamine concentration, applied voltage, and capillary temperature on the enantioseparation were systematically investigated. Under the optimized conditions, thirteen pairs of enantiomers were baseline resolved and five pairs of enantiomers were partially enantioseparated. Salbutamol showed a sign of separation with a shoulder peak. A reversal of propranolol enantiomer migration orders took place in the case when different concentrations of triethylamine were added into the NACE running buffers. The mass spectrometry (MS) results confirmed that triethylamine could promote the formation of negatively charged L-sorbose–boric acid complex chiral counter ions with different complex ratios. The enantioseparation results were compared with the previous work. Calibration curves showed excellent linearity with square of correlation coefficients (r2) greater than 0.9994 over concentration ranges of 5.0–500.0 μg mL−1 for each enantiomer of clenbuterol and esmolol, and 12.5–500.0 μg mL−1 for that of metoprolol. The limits of detection (LODs) and limits of quantitation (LOQs) for each enantiomer were 0.4–1.25 μg mL−1 and 1.5–4.0 μg mL−1, respectively. The relative standard deviations (RSDs) of intra-day and inter-day precisions of migration times were ≤1.64% (n = 6), and ≤6.54% (n = 15), respectively. The peak areas were ≤4.03% (n = 6), and ≤3.92% (n = 15), respectively. This method can likely be applied to the determination of each enantiomer in pharmaceutical formulations.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...