Enzymeless biosensor based on β-NiS@rGO/Au nanocomposites for simultaneous detection of ascorbic acid, epinephrine and uric acid†
Abstract
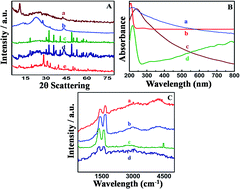
In this study, marigold flower-like self-assembled β-NiS (nickel sulfide) nanosheets were grown on rGO (reduced graphene oxide) by a single-step hydrothermal process and then gold nanospheres (AuNS) were electrochemically deposited on the β-NiS@rGO nanostructures. The β-NiS@rGO/AuNS hierarchical hybrid demonstrates excellent electrochemical activities for clinically important analytes such as AA (ascorbic acid), EP (epinephrine) and UA (uric acid) simultaneously. Moreover, the β-NiS@rGO/AuNS/GCE exhibits significant detection of AA by one order and UA by two orders higher sensitivity when compared to a β-NiS@rGO modified electrode. We investigated using this electrocatalyst for individual detection, the linear responses of AA, EP and UA at concentrations in the ranges of 900 nM to 100 μM, 2 μM to 1 mM and 100 nM to 1 mM with low detection limits of 331 nM, 540 nM and 4.5 nM (S/N = 3σ/b), respectively; the resulting non-enzymatic biosensor also retained a good response to simultaneous detection with a wide linear range 1 μM to 1 mM, 2 μM to 1 mM and 100 nM to 1 mM and significantly lower detection limits of 682 nM, 1.3 μM and 6 nM, respectively. Excellent stability, reproducibility, and selectivity were achieved. Biosensing of AA, EP and UA in human urine, blood, serum, fruits and pharmaceutical drugs was successfully demonstrated without any preliminary treatment.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...