Effect of incorporation of boron nitride nanoparticles on the oxygen barrier and thermal properties of poly(3-hydroxybutyrate-co-hydroxyvalerate)
Abstract
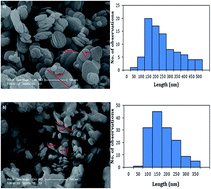
In this study poly(3-hydroxybutyrate-co-3-hydroxyvalerate) and boron nitride (PHBV/BN) nanobiocomposites were prepared by incorporating various percentages of boron nitride using extrusion processing. The oxygen permeation properties of the PHBV nanocomposites were examined to compare their oxygen-barrier performance as affected by temperature and nanoparticle content. The resulting PHBV nanocomposites showed an increase in oxygen permeability as temperature increased, with an Arrhenius behavior, and an activation energy of 54.1 kJ mol−1 and 57.5 kJ mol−1 for neat PHBV and PHBV3BN composites, respectively. The barrier properties of the composites decreased with BN addition and reached 1.22 ± 0.06 (cm3 mm m−2 per day per atm) at 3 wt%. Thermal stabilities of the prepared nanobiocomposites were measured by thermogravimetric analysis (TGA) and it was found that the thermal stability of the composites was higher than that of neat PHBV. The differential scanning calorimetry results indicated that the addition of BN nanoparticles to the composites increased their crystallinity.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...