An efficient method for tylosin removal from an aqueous solution by goethite modified straw mass
Abstract
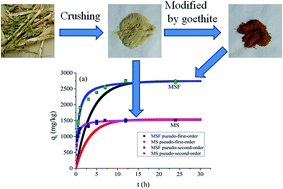
Renewable agricultural residues are produced in large quantities as waste, and their storage and management create environmental problems. Similarly, antibiotics could cause harm to the ecosystem and to the growth of plants and animals. As one of the widely used antibiotics in the world, the environmental risks of tylosin (TYL) are receiving increasing attention. In order to find a clean and effective method for TYL removal from an aqueous solution, maize straw (MS) is modified by goethite and the sorption capacity of the natural and modified forms (MSF) is determined for TYL removal. The characterisations of MS and MSF were carried out by XRD, FTIR, XPS and SEM-EDS. The characteristics of the sorption behavior of TYL on MS and MSF are systematically investigated. The results indicate that the sorption capacity of TYL on MSF is significantly higher than MS, and the sorption kinetics data of TYL on MS and MSF well fits the pseudo-second-order kinetics model and the sorption isotherms data well fits the linear model. Moreover, the sorption thermodynamics of TYL on MSF and MS indicate that a high temperature could favor the sorption of TYL on MS and MSF. In addition, the sorption of TYL on MS and MSF can be affected by pH and ionic strength of the solution. The sorption mechanisms of TYL on MS mainly involve electrostatic interactions and hydrophobic interactions, whereas electrostatic interactions, H bonding, hydrophobic interactions and surface complexation play a primal role in the sorption of TYL on MSF.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...