A new parameter for the stimulation effect and its application in the prediction of the hormetic effect in chemical mixtures†
Abstract
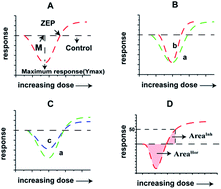
It is important and necessary to study the prediction methods for chronic mixture toxicity at low concentration, particularly mixtures containing chemicals with hormetic effects because pollutants in the real environment exist at low-doses in the form of mixtures. However, this issue is restricted by the question of how to accurately quantify the size of the hormetic effect. The available parameters to qualify the hormetic effect, including the maximum stimulation effect (Ymax) and maximum stimulation effect concentration (M), only characterize the vertical characteristics (effect characteristics) or horizontal variation (concentration characteristics), respectively. A parameter considering both the vertical characteristics and horizontal variation, named “integrated area” (AreaSim), which is the closed area of the fitting curve and abscissa axis (Y = 0) to symbolize the size of the stimulation effect at low concentrations, was raised based on the toxicity mechanism of sulfonamides (SAs) on Vibrio fischeri. Furthermore, the calculation method of integrated area for mixtures was formulated based on the integrated area for a single chemical as follows: AreaSim-mix = aAreaSim-A + bAreaSim-B + c. Then, this formula was applied in different mixed systems containing different chemicals on different organisms, and different formulas were devised. All of the above formulae have good correlation, which implies the general applicability of the integrated area for mixtures. This study provides a new method to accurately determine the size of the hormetic effect of a single chemical and a prediction equation for the hormetic effect in mixtures.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...